Glaucoma Treatment
Why is Glucoma so dangerous?
Glaucoma is the second major cause of blindness in the world. It has no early symptoms. Very often loss of peripheral vision brings the problem to light. Loss of vision due to glaucoma cannot be reversed. Acute glaucoma may cause instant blindness.
We have the complete set up for detection and treatment of Glaucoma. We are also continuously upgrading our facilities to ensure that the latest treatments in glaucoma care are available to you.
EARLY DETECTION IS THE KEY TO PREVENT BLINDNESS.
Your eye examination for glaucoma at Poona Eye Care will involve modern technology, which can detect glaucoma well before it starts affecting your vision. Tonometry is used to measures inner pressure of the eye, while ophthalmoscopy analyses the inside of the eye under magnification.
Additional tests which may be used include perimetry test and gonioscopy. We have facility for Optical Coherence Tomography for multi-layered imaging of the optical nerve.
Drag ![]() left/right for full view
left/right for full view


| Normal Vision | Glaucoma Vision |
Drag ![]() left/right for full view
left/right for full view


| Normal Vision | Glaucoma Vision |
WE TEST YOU REGULARLY ON A PRE-PLANNED SCHEDULE
We plan out a schedule based on your risk factors and decide the frequency of eye-examination and testing to ensure that we don't miss any symptoms.
WE ARE KEEN TO TREAT GLAUCOMA WITH NON-SURGICAL METHODS
Our experts have long experience in non-surgical glaucoma treatment options. Many of our patients avoid surgery through our glaucoma management medication programme.
WE HAVE FACILITIES FOR ALL SURGICAL MODALITIES
We have facilities and trained surgeons for laser surgery, trabeculectomy and shut implants. Our team of qualified and trained surgeons has long years of experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can glaucoma lead to total blindness?
Yes. Initially there is peripheral loss of vision and if not treated it eventually results in total blindness. In the more acute type of glaucoma, onset of blindness can be sudden and irreversible, if not prevented through early medical intervention.Glaucoma is the second leading cause of blindness all over the world.
What causes glaucoma?
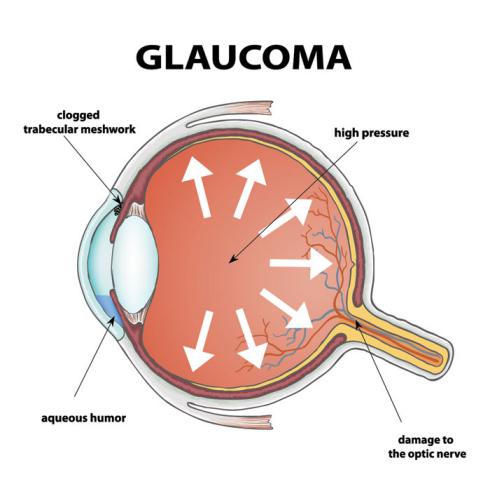
The eye is connected to the brain by a nerve called the optic nerve. Glaucoma is caused by damage to the optic nerve due to an increase in the production of aqueous fluid.
(This is image is taken from the Internet.)
Why does the optic nerve get damaged?
- The most common cause of damage to the optic nerve is ‘ increased pressure in the eye’. This increased pressure is caused by malfunction in the flow of the eye-fluid. The eye has a clear fluid which flows continuously in the eye. The fluid leaves the eye at the open angle where the cornea and iris meet. (See diagram below.) When the fluid reaches the angle, it flows through a spongy meshwork, like a drain, and exits the eye. When for some reasons, the fluid cannot flow out properly from at this angle, it accumulates inside the eye. This increases intra-ocular pressure leading to nerve damage.
- Other causes for glaucoma are a blunt or chemical injury to your eye, severe eye infection, blocked blood vessels inside the eye or inflammatory conditions. It’s rare, but sometimes eye surgery to correct another condition can bring it on. But these causes are rare.
What are the different types of Glaucoma?
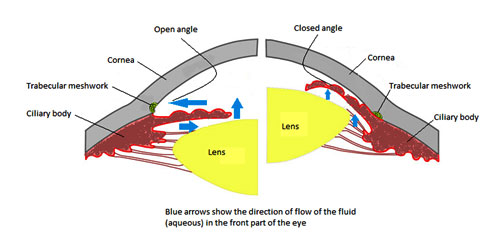
Open Angle Glaucoma
In Open Angle Glaucoma the trabecular (spongy) meshwork (the drain) functions very slowly. Due to the slow flow, fluid gets accumulated within the eye increasing eye pressure. When this pressure reaches the optic nerve, it can get damaged.
This is the most common type of glaucoma. It happens gradually.This type of glaucoma is painless and causes no vision changes at first. Changes, when they come, first affect the peripheral vision. Some people can have optic nerves that are sensitive to normal eye pressure. This means their risk of getting glaucoma is higher than normal. Regular eye examinations are important to find early signs of damage to their optic nerve.
Closed-angle glaucoma/narrow-angle glaucoma
This type of glaucoma happens when the iris is very close to the drainage angle. The iris can end up blocking the drainage angle. When the drainage angle gets completely blocked, eye pressure rises very quickly causing an emergency acute attack. This attack needs urgent attention as it can lead to blindness very quickly.
Signs of an acute closed angle glaucoma attack:
- Vision turns blurry very suddenly
- Severe eye pain
- Headache
- Nausea
- vomit
- Rainbow-colored rings or halos around lights
Some people develop closed angle glaucoma very slowly. This is called chronic closed angle glaucoma.
(This image is taken from the internet.)
Who should be tested for glaucoma?
Those with a history of glaucoma in the family should get tested for glaucoma once a year. For those without a history and under 40, it is enough to test for glaucoma once in five years. As age advances, this period should go to once in two to three years.
How is glaucoma diagnosed?
A comprehensive glaucoma examination should include:
| Examining… | Name of Test |
| The shape and color of the optic nerve | Ophthalmoscopy(dilated eye exam) |
| The complete field of vision | Perimetry(visual field test) |
| The angle in the eye where the iris meets the cornea | Gonioscopy |
| Thickness of the cornea | Pachymetry |
Another test called the Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) is a non-invasive imaging test which examines the optical nerve.
How is glaucoma treated?
Glaucoma can be treated with eye drops, pills, surgery or a combination of all these things. When detected early, there is no loss of vision with proper treatment.
Eye drops form the first line of treatment if the problem is in its early stages. It is important to follow the doctors instructions very thoroughly for good long term benefits. If eye-drops are unable to control intra-ocular pressure, pills form the next line of treatment. Both eye-drops and pills can have side-effects and therefore regular meetings with the optholmologist and proper management of treatment are important.
If medications do not achieve the desirable results, or their side-effects are not manageable, surgery is thought of.
Laser procedure
Laser procedure is an intermediate step between drugs and traditional surgery.The laser beam (a high energy light beam) is focused upon the eye's drain. This can change the eye’s drainage system in very subtle ways so that aqueous fluid is able to pass more easily out of the drain. It’s a quick procedure and your routine activities can start from the next day. There are different types of laser procedures. The lasers that deal with open angle glaucoma are directed towards treating the trabecular meshwork. For closed angle glaucoma, laser procedure is used to design a bypass to the usual path of fluid flow which is blocked. Many patients get considerable relief after laser procedure.
Traditional incisional surgery
The most popular traditional surgery is called trabeculectomy. It is used for both open angle and closed angle glaucoma. Here the surgeon creates a small passage for draining out excess eye fluid. To reduce the possibility of the body’s response system scarring and thereby closing the passage created by the surgeon, surgery is performed with anti-fibrotic agents. 50% of the patients no longer require glaucoma medication for a long time after this surgery. Trabeculectomy is a short procedure and patients can be discharged after a few hours of observation. The recovery time is from four weeks to two months.
Shunt implant surgery
Another type of surgery which introduces tube shunts for free flow of drain is now gaining in popularity. Tube shunt is a flexible glaucoma drainage device that is implanted in the eye to divert aqueous humor (the fluid inside the eye) from the inside of the eye to an external reservoir.The fluid that collects in the reservoir is then absorbed by the eye’s own veins and transported out of the eye cavity.The tube shunt is made of silicone or polypropylene. The entire implant is covered with the eye’s own external covering.
There are several different types of tube shunts available. Shunt is selected based on the specific eye condition and surgeon’s preference. The Ahmed Glaucoma Valve(Shunt) is the most commonly used type of shunt.
Cycloablation
If traditional/shunt surgery is unable to deliver the results, or is seen as unlikely to produce relief, a laser procedure called cycloablation is available. Here a part of the ciliary body, which produces the fluid is destroyed (ablated) with laser. This is a realtively new procedure and is done only when nothing else works.
What to expect during a glaucoma surgery?
The laser procedure is usually performed in an eye doctor’s clinic. Before the surgery, your eye will be numbed with medicine. Your eye may be a bit irritated and your vision slightly blurry after the surgery. You should arrange a ride home after your surgery.In general, patients can resume normal daily activities the next day after laser surgery.
Traditional incisional surgery is also a day procedure. The conventional glaucoma surgery recovery time is longer than that of the laser procedure. Typically, recovery requires two to four weeks; however, it may take up to two months for glaucoma surgery results to become apparent and vision to stabilize.
What are the risks in glaucoma surgery?
Risks of Laser Surgery
As with any type of surgery, laser surgery can carry some risks. Some people experience a short-term increase in their intraocular pressure (IOP) soon after surgery. In others who require YAGCP (Cyclophoto-Coagulation) surgery, there is a risk of the IOP dropping too low to maintain the
eye’s normal metabolism and shape. The use of anti-glaucoma medication before and after surgery can help to reduce this risk.There is a small risk of developing cataracts after some types of laser surgery for glaucoma. However, the potential benefits of the surgery usually outweigh any risks.
Incisional surgery & shunt implants
Complications that may result from this surgery include early and late bleb leaks, blebitis and endophthalmitis (infections), hypotony (low IOP), flat anterior chambers, choroidal detachments (swelling or bleeding behind the retina associated with low pressure), retinal detachments, corneal edema, and permanent visual loss.
Shunts are much less likely to suffer a bleb leak, but have increased risk of corneal edema and erosion of the tube is a possibility. Shunts may need replacement with time. Diplopia (double vision) is also described with tube shunts. Both procedures increase the risk of developing cataracts. However, these are all rare possibilities and are usually outweighed by benefits from surgery. Risk analysis is done on a case to case basis and circumstances in every case can vary vastly.
Other treatments at Poona Eye Care
Please do write to us if you have any more queries on this. We will be glad to assist.
CONTACT US

- Shop No. 1, Lajawanti Apartments, 62/9 Erandawane, Opposite Sonal Hall, Karve Road, Pune-411004, Maharashtra, India.
- +91 735-027-7779
- info@poonaeyecare.com
Working Hours
- MON: 9:00 AM - 08:00 PM
- TUES: 9:00 AM - 08:00 PM
- WED: 9:00 AM - 08:00 PM
- THUR: 9:00 AM - 08:00 PM
- FRI: 9:00 AM - 08:00 PM
- SAT: 9:00 AM - 01:00 PM